Is this your first visit to this site? Let me set you up on what this is all about.
What is this?
The Post Tomorrow Land's Morning Post is an experimental, hyper-local, multilingual, and automated post-fictional news portal envisioning speculative futures. It is crafted using large language models informed by climate models and scenarios. It uses a range of climate scenarios and selected climate model projections converted into a 7-day weather forecast for today 50 years into the future to prompt large language models. These models then generate speculative future scenarios presented in the format of an online newspaper.
What are those scenarios?
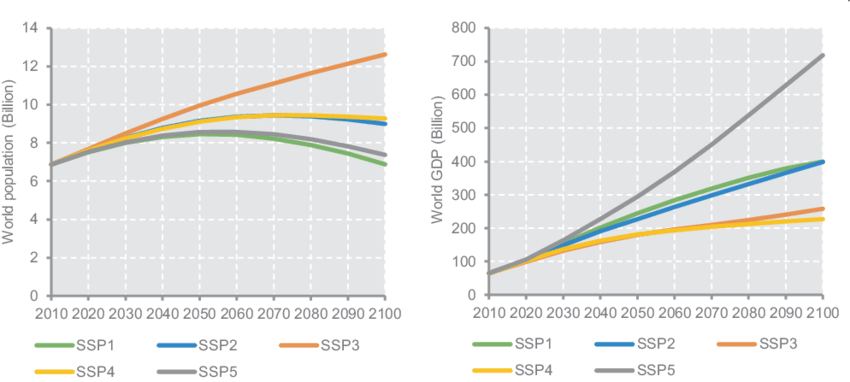
Shared Socioeconomic Pathways (SSPs) are climate change scenarios of projected socioeconomic global changes up to 2100 as defined in the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report on Climate Change in 2021. They are used to derive greenhouse gas emissions scenarios with different climate policies. The SSPs provide short narratives describing alternative developments and quantitative scenarios, numbers, and assumptions such as population, urbanization, emissions, and GDP derived from Integrated assessment models (IAM). These numbers constitute the parameters to run the physical simulations of climate models such as coupled atmosphere–ocean-sea ice global circulation models (GCM) or Earth System models (ESM)
You can select SSP and climate model in the weather widget on the upper right. Hereyou also find a link to the 7-day weather forecast.

How are those pathways described?
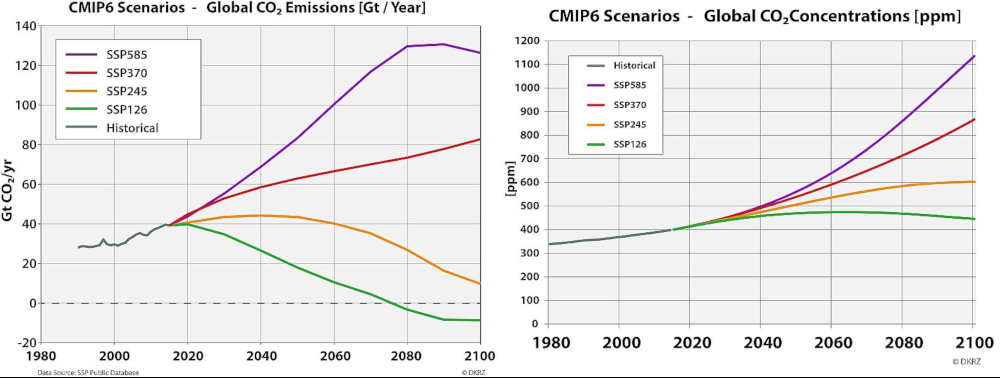
The names of these scenarios consist of the SSP on which they are based (SSP1-SSP5), combined with the expected level of radiative forcing in the year 2100 (2.6 to 8.5 W/m2). The pathways are described as follows:
SSP126: Sustainability (Taking the Green Road)
The world shifts gradually, but pervasively, toward a more sustainable path, emphasizing more inclusive development that respects predicted environmental boundaries. Management of the global commons slowly improves, educational and health investments accelerate the demographic transition, and the emphasis on economic growth shifts toward a broader emphasis on human well-being. Driven by an increasing commitment to achieving development goals, inequality is reduced both across and within countries. Consumption is oriented toward low material growth and lower resource and energy intensity.
--
low GHG emissions: CO2 emissions cut to net zero around 2075
Estimated warming by 2100: 1.8°C
SSP245: Middle of the Road
The world follows a path in which social, economic, and technological trends do not shift markedly from historical patterns. Development and income growth proceeds unevenly, with some countries making relatively good progress while others fall short of expectations. Global and national institutions work toward but make slow progress in achieving sustainable development goals. Environmental systems experience degradation, although there are some improvements and overall the intensity of resource and energy use declines. Global population growth is moderate and levels off in the second half of the century. Income inequality persists or improves only slowly and challenges to reducing vulnerability to societal and environmental changes remain."
--
intermediate GHG emissions: CO2 emissions around current levels until 2050, then falling but not reaching net zero
Estimated warming by 2100: 2.7 °C
SSP370: Regional Rivalry (A Rocky Road)
A resurgent nationalism, concerns about competitiveness and security, and regional conflicts push countries to increasingly focus on domestic or, at most, regional issues. Policies shift over time to become increasingly oriented toward national and regional security issues. Countries focus on achieving energy and food security goals within their own regions at the expense of broader-based development. Investments in education and technological development decline. Economic development is slow, consumption is material-intensive, and inequalities persist or worsen over time. Population growth is low in industrialized and high in developing countries. A low international priority for addressing environmental concerns leads to strong environmental degradation in some regions.
--
high GHG emissions: CO2 emissions double
Estimated warming by 2100: 3.6 °C
SSP585: Fossil-fueled Development (Taking the Highway)
This world places increasing faith in competitive markets, innovation and participatory societies to produce rapid technological progress and development of human capital as the path to sustainable development. Global markets are increasingly integrated. There are also strong investments in health, education, and institutions to enhance human and social capital. At the same time, the push for economic and social development is coupled with the exploitation of abundant fossil fuel resources and the adoption of resource and energy intensive lifestyles around the world. All these factors lead to rapid growth of the global economy, while global population peaks and declines in the 21st century. Local environmental problems like air pollution are successfully managed. There is faith in the ability to effectively manage social and ecological systems, including by geo-engineering if necessary.
--
very high GHG emissions: CO2 emissions triple by 2075
Estimated warming by 2100: 4.4 °C
Read more about SSPs on Wikipedia or Carbonbrief
What now?
Go read your speculative future or more about who made it

